AN INTACT, FULL-THICKNESS BARRIER FOR OPTIMAL PROTECTION
Lacking an appropriate protective barrier following surgical intervention may result in susceptibility to further degradation or slower healing of underlying tissue, as well as loss of physical separation between adjacent tissues due to the formation of post-operative adhesions.1-4
Using a protective barrier, such as ACMShield, following surgical intervention aids in maintaining temporary physical protection and separation between the repaired structure, such as a nerve or tendon, and adjacent tissue.
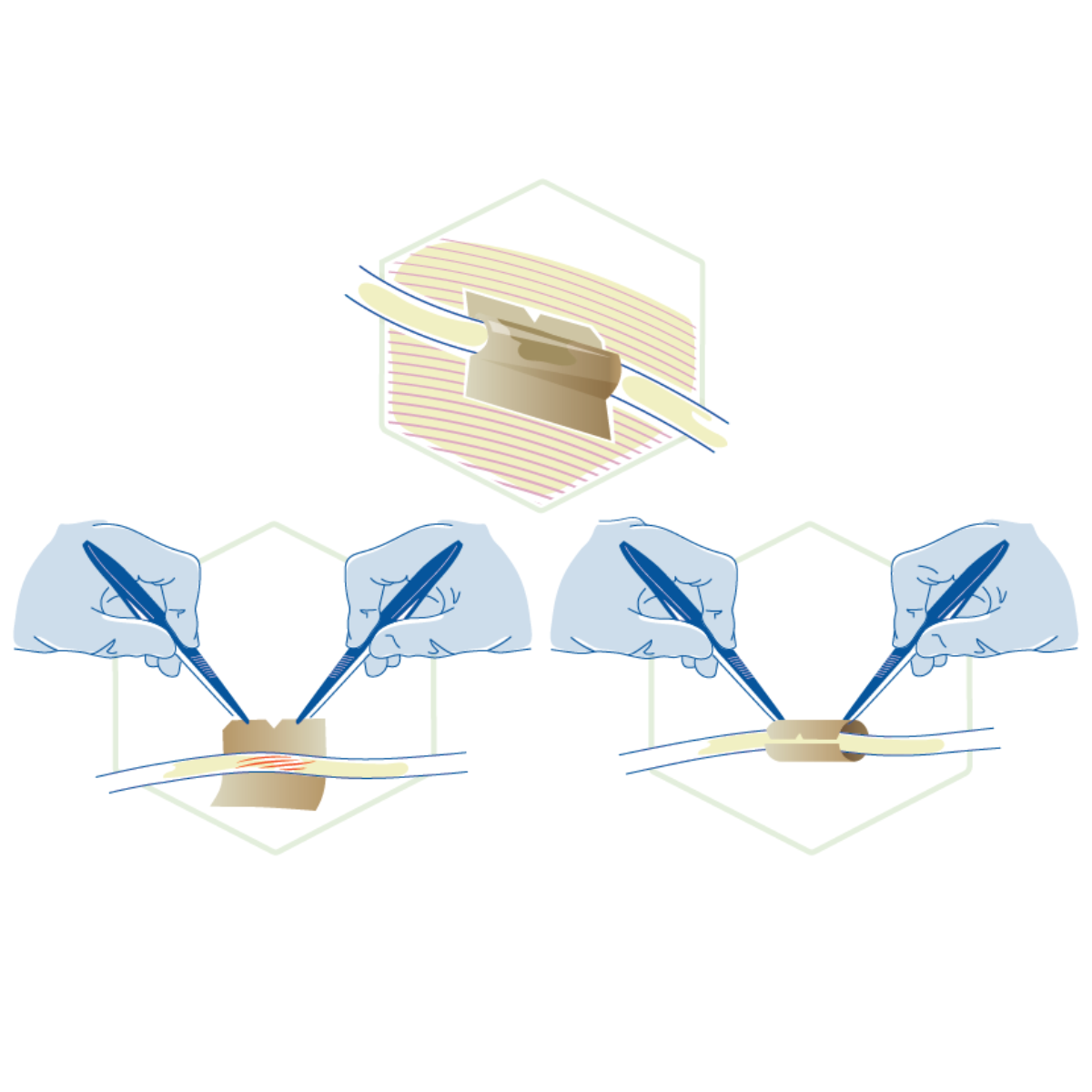
ACMShield Advantages
- Includes the complete amnion and chorion layers, including the epithelial and spongy layers, for improved handling
- Minimal processing preserves native structure and benefits of amniotic tissue
- Rapid rehydration in situ
- Self-adherent, but fixation may be used by method of choice, if desired
- Multiple sizes for a variety of surgical applications
- 5-year shelf life with ambient temperature storage
- Terminally sterilized for patient safety

Sizing Information
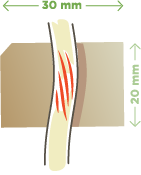
ACM2030
20 mm x 30 mm
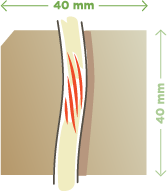
ACM4040
40 mm x 40 mm

ACM4060
40 mm x 60 mm
Try ACMShield Soft Tissue Barrier
Request a demo or trialRELATED INFORMATION
CHECKPOINT®
Intraoperative Stimulators
CHECKPOINT EDGE™
Nerve Cutting Kit

NERVE EDUCATION
REFERENCES
1. Dy CJ, Aunins B, Brogan DM. Barriers to Epineural Scarring: Role in Treatment of Traumatic Nerve Injury and Chronic Compressive Neuropathy. J Hand Surg Am. 2018;43(4):360-367. 2. Wang ML, Rivlin M, Graham JG, Beredjiklian PK. Peripheral nerve injury, scarring, and recovery. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;60(1):3-9. 3. Khanna A, Friel M, Gougoulias N, Longo UG, Maffulli N. Prevention of adhesions in surgery of the flexor tendons of the hand: what is the evidence? Br Med Bull. 2009;90:85-109. 4. Titan AL, Foster DS, Chang J, Longaker MT. Flexor Tendon: Development, Healing, Adhesion Formation, and Contributing Growth Factors. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(4):639e-647e.